The Complete Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Certification

Understanding Diamond Certification: Your Key to Confident Purchases
When investing in a lab-grown diamond, certification is your assurance of quality and authenticity. At Labrilliante, we believe educated customers make confident decisions, which is why we've created this comprehensive guide to diamond certification.
The Role of Certification Laboratories
Diamond certification is conducted by independent gemological laboratories that analyze and document a diamond's characteristics. For lab-grown diamonds, the primary certification bodies include:
- GIA (Gemological Institute of America): The most globally recognized authority, now fully certifying lab-grown diamonds with specialized reports
- IGI (International Gemological Institute): Pioneers in lab-grown diamond certification with detailed documentation
- GCAL (Gem Certification & Assurance Lab): Known for their comprehensive light performance analysis
The Certification Process Demystified
The certification process involves multiple scientific examinations performed by trained gemologists. Each diamond undergoes rigorous testing to document its characteristics:
- Initial examination and cleaning
- Weight measurement using precision scales
- Color grading under controlled lighting conditions
- Clarity assessment using 10x magnification
- Cut analysis with specialized equipment
- Origin verification (lab-grown vs. natural)
- Final documentation and security features implementation
GIA vs. IGI vs. GCAL: Lab-Grown Certification Nuances
Each laboratory has distinct approaches to lab-grown diamond certification:
Lab-Grown Diamond Certification Bodies Comparison
| Certification Body | Lab-Grown Terminology | Special Features | Avg. Cost Premium |
|---|---|---|---|
| GIA Gemological Institute of America | "Laboratory-Grown" | Origin detection technology | 15-20% |
| IGI International Gemological Institute | "Laboratory-Grown" | Detailed inclusion maps | 5-10% |
| GCAL Gem Certification & Assurance Lab | "Laboratory-Grown" | Light performance analysis | 10-15% |
| Note: Premium percentages represent average increased costs compared to uncertified diamonds of similar specifications. | |||
IGI's reports often provide more detailed growth method information (CVD or HPHT), while GIA focuses on rigorous origin verification. GCAL stands out with their light performance analysis, measuring brilliance and fire objectively.
How to Spot Fake or Inaccurate Certificates
Authentic certificates include multiple security features:
- Holographic elements that change when tilted
- Unique certification number that can be verified online
- Microprinting that cannot be easily reproduced
- QR codes linking to official verification pages
At Labrilliante, we recommend always verifying your certificate on the issuing laboratory's official website before purchase. Many labs offer instant verification tools where you can enter the report number and confirm the certificate's authenticity.
Case Study: Understanding Your Certificate
Below is a sample comparison of certification documents from different labs for similar lab-grown diamonds:

The 4Cs Grading System: Understanding Quality Metrics in Lab-Grown Diamond Certification
The 4Cs—Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight—form the universal standard for evaluating diamonds. However, these metrics have unique considerations when applied to lab-grown diamonds on certification documents.
Cut Certification & Light Performance
The cut grade remains the most influential factor affecting a diamond's brilliance and value, regardless of origin. However, certification bodies evaluate lab-grown diamonds with specific considerations:
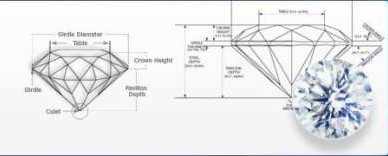
Cut Proportions on Lab-Grown Certificates:
- Table percentage (53-58% ideal for round brilliants)
- Depth percentage (59-62.5% optimal range)
- Crown and pavilion angles (critical for light return)
- Girdle thickness (affects durability and apparent size)
At Labrilliante, we prioritize excellent and ideal cut grades, as they maximize the diamond's inherent brilliance—a quality particularly achievable in lab-grown diamonds due to their controlled growth environment.
Light Performance Metrics: Modern certification reports, especially from GCAL, may include specialized light performance analysis:
- Brilliance (white light return)
- Fire (spectral color dispersion)
- Scintillation (sparkle and pattern of light and dark areas)

Clarity Grading Specifics for Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds display unique inclusion patterns that can actually help identify their origin. Certification reports document these characteristics differently than for natural diamonds:
Lab-Grown Diamond Clarity Characteristics by Growth Method
| Growth Method | Typical Inclusions | How They Appear on Certificates |
|---|---|---|
| HPHT High Pressure High Temperature | Metallic flux inclusions | Noted as "metallic" on clarity plots |
| HPHT High Pressure High Temperature | Crystal inclusions | Small geometric shapes on plots |
| CVD Chemical Vapor Deposition | Growth striations | Parallel lines indicated on diagrams |
| CVD Chemical Vapor Deposition | Cloud inclusions | Clustered pinpoints marked as areas |
| Certification Impact: These inclusion patterns help laboratories definitively identify lab-grown origin and specific growth method. | ||
Reading Clarity Plots: Certification clarity plots use standardized symbols to indicate the type and location of inclusions:
- Crystals: small geometric shapes
- Clouds: dotted outlines
- Feathers: irregular lines
- Needles: thin straight lines

Color Grading Nuances
While natural diamonds are graded on a D (colorless) to Z (light yellow) scale, lab-grown diamonds present unique considerations in color certification:
- D-F Color Grades: Previously challenging to achieve in lab-grown diamonds, technological advances now allow Labrilliante to offer these premium colorless grades
- G-J Near-Colorless: Often representing the best value proposition in lab-grown diamonds
- Fancy Colors: Lab-grown diamonds can be produced in vibrant fancy colors through controlled introduction of specific elements during growth
Fluorescence Notes on Certificates: Fluorescence (the diamond's reaction to UV light) is documented on certificates and can affect appearance:
- None/Negligible: No visible reaction under UV light
- Faint/Medium: Slight blue glow under UV, generally not visible in normal lighting
- Strong/Very Strong: Noticeable blue glow under UV light, may affect appearance
Color Consistency: Lab certification reports may note color zoning or distribution, particularly in CVD-grown diamonds, which can sometimes display subtle banding patterns.
Carat Weight Considerations
Carat weight (1 carat = 0.2 grams) is measured with precision scales accurate to the hundredth of a carat. On lab-grown diamond certificates, you'll find:
- Exact weight to two decimal places (e.g., 1.05 carats)
- Measurements in millimeters (length, width, depth)
- Calculated average diameter for round diamonds
While weight accuracy is consistent across certification bodies, it's worth noting that lab-grown diamonds can be created in precise target weights to optimize value, something not possible with natural diamonds.

Diamond Inspection Techniques: Expert Methods to Verify Your Lab-Grown Diamond
Understanding how to properly inspect lab-grown diamonds empowers you to verify certification accuracy and make informed purchase decisions. At Labrilliante, we believe in transparency about the evaluation processes that ensure our diamonds meet exacting standards.
Professional Examination Tools & Methods
Gemologists use specialized equipment to evaluate diamonds beyond what's visible to the naked eye:
Laboratory Growth Method Detection Techniques
Diamond Examination Tools & Their Applications
| Tool | Purpose | What It Reveals |
|---|---|---|
| 10x Loupe Basic magnification | Magnification of surface features | Inclusions, surface blemishes, facet alignment |
| Microscope 40-60x magnification | Detailed internal examination | Growth patterns, inclusion types, crystal structures |
| Diamond Tester Electronic device | Thermal conductivity testing | Basic material verification |
| Advanced Spectrometers Laboratory equipment | Light absorption patterns | Definitive identification of lab-grown origin |
| UV Light Source Specialized lighting | Fluorescence examination | Growth method indicators, treatment detection |
| DiamondView™ De Beers technology | Fluorescence imaging | Growth structure visualization |
| Professional Application: Certification laboratories employ all these tools in sequence to comprehensively analyze lab-grown diamonds. | ||
Growth Pattern Analysis: Different manufacturing methods create distinct internal structures that certification laboratories document:
- HPHT diamonds typically show cubic or octahedral growth sectors
- CVD diamonds display layered, planar growth structures

Consumer-Friendly Verification Methods
While professional tools provide definitive analysis, several consumer-level tests can help verify your diamond and its certification:
The Breath Test:
- Hold the clean diamond between your fingers
- Exhale a small puff of breath onto the diamond
- Observe how quickly the fog disappears
- Results: Real diamonds (lab-grown or natural) disperse heat rapidly, causing the fog to vanish almost instantly
DIY Setting & Prong Inspection Guide:
- Use magnifying glass (10x minimum) in good lighting
- Check prong security by gently moving the setting
- Examine metal quality around the diamond
- Verify that certificate numbers match any laser inscriptions (typically on girdle)
Lighting Tests Anyone Can Perform:
- Sparkle test: Under bright light, a well-cut diamond will display vibrant rainbow colors (fire) and bright white light return (brilliance)
- Shadow test: Place the diamond over newspaper—you shouldn't be able to read through a real diamond

When to Trust vs. Question Certifications
Certification provides confidence, but knowing when additional scrutiny is warranted protects your investment:
Green Flags - Signs of Trustworthy Certification:
- Certificates from major laboratories (GIA, IGI, GCAL)
- Matching details between certificate and physical diamond
- Presence of security features on certificate
- Successful online verification of certificate number
- Laser inscription that matches certificate number
Red Flags - When Additional Verification Is Needed:
- Certificate from unknown or non-established laboratories
- Vague terminology about diamond origin
- Missing growth method information
- Certificate looks photocopied or lacks security features
- Significant price discrepancies compared to similar certified diamonds
- Absence of laboratory website verification option
At Labrilliante, we encourage customers to compare their physical diamond's characteristics with the certification documentation. The proportions, measurements, and identifiable inclusions should align precisely with what's documented on your certificate.
When Certification Details Might Diverge: Minor differences in measurements (within 0.02mm) are acceptable due to different measuring techniques. However, color and clarity grades should never differ by more than one grade from what's stated on the certificate.
Lab-Grown Diamond Technology: Understanding How Manufacturing Methods Impact Certification
The technology behind lab-grown diamonds directly influences their physical properties and how they're documented on certification reports. At Labrilliante, we believe understanding these processes helps our customers appreciate the unique qualities of their lab-grown diamonds.
CVD vs. HPHT: Growth Methods & Their Certification Markers
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): This advanced process creates diamonds by depositing carbon atoms onto a substrate in a vacuum chamber filled with carbon-rich gas:
- Growth Pattern Indications on Certificates:
- Linear growth striations (parallel lines)
- Potential "strain" patterns noted in observations
- Occasional subtle color banding mentioned in comments
- Certificate Terminology for CVD Diamonds: Laboratory reports typically identify these as "CVD-grown," "Laboratory-grown using CVD method," or simply "CVD" in the comments section.
High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT): This process mimics the natural diamond formation environment using extreme pressure and heat:
- Growth Pattern Indications on Certificates:
- Cuboctahedral growth sectors
- Metallic inclusions (nickel, iron, cobalt) noted in comments
- Magnetic properties sometimes mentioned
- Certificate Terminology for HPHT Diamonds: Reports identify these as "HPHT-grown," "Laboratory-grown using HPHT method," or "HPHT" in technical notes.
How Certification Laboratories Detect Growth Methods
Modern laboratories employ sophisticated techniques to identify growth methods:
Laboratory Growth Method Detection Techniques
| Detection Method | What It Reveals | How It Appears on Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Photoluminescence Light emission analysis | Crystal lattice impurities unique to each growth method | Growth technique noted in comments section |
| DiamondView™ imaging Specialized fluorescence | Fluorescence patterns that differ between CVD/HPHT | Special comments about growth structure |
| FTIR spectroscopy Infrared analysis | Nitrogen concentration and aggregation state | Noted in laboratory report comments |
| Cross-polarized light Strain visualization | Strain patterns characteristic of growth method | Mentioned in technical observations |
| Certification Implication: These scientific methods ensure accurate identification of both diamond origin and specific manufacturing process. | ||
Certification Laboratories' Approach: GIA's laboratory-grown diamond reports include specific sections identifying growth method, while IGI provides detailed comments about growth structure. GCAL often includes photomicrographs showing characteristic features.
Why Some Lab-Grown Diamonds Fail Standard Testers
Understanding why traditional diamond testers might misidentify lab-grown diamonds helps clarify certification importance:
HPHT Conductivity Issues: Traditional thermal conductivity testers may struggle with HPHT lab-grown diamonds because:
- Some HPHT diamonds contain trace metallic elements that affect electrical conductivity
- These can occasionally give false "moissanite" readings on basic testers
- Modern certification explicitly addresses this with conductivity testing notes
CVD Detection Challenges: CVD diamonds typically pass traditional diamond testers because:
- Their thermal conductivity closely matches natural diamonds
- They contain minimal metallic inclusions
- Only advanced spectroscopic testing can definitively identify them
Certificate Documentation: Reputable certification reports will document any properties that might affect standard testing methods, ensuring consumers understand their diamond's unique characteristics.

Post-Growth Treatments & Certification Disclosure
Certification reports meticulously document enhancements applied after the initial growth process:
Color Treatments:
- HPHT color enhancement (pressure and heat to improve color)
- Irradiation (to create fancy colored diamonds)
Clarity Treatments:
- Laser drilling (to remove dark inclusions)
- Fracture filling (to improve apparent clarity)
All legitimate certification bodies require full disclosure of these treatments, which will appear prominently on reports. At Labrilliante, we prioritize transparency by offering primarily untreated lab-grown diamonds with comprehensive certification.
Post-Growth Treatment Documentation on Certificates
| Treatment Type | Certificate Terminology | Location on Certificate |
|---|---|---|
| HPHT Color Treatment Heat and pressure process | "HPHT processed" or "Color treated" | Comments section, often in bold |
| Irradiation Color enhancement | "Irradiated to produce color" | Comments section |
| Laser Drilling Inclusion removal | "Clarity enhanced" or "Laser drilled" | Comments section |
| Fracture Filling Clarity improvement | "Clarity enhanced" or "Fracture filled" | Comments section, usually prominent |
| Disclosure Requirement: All legitimate certification requires full transparency about treatments, which can significantly affect value. | ||
When reviewing certificates, Labrilliante recommends paying particular attention to these disclosure sections, as treatments can significantly impact a diamond's value and long-term performance.

The Smart Buyer's Guide to Certified Lab-Grown Diamonds
Making an informed purchase decision requires understanding how certification impacts value, quality assurance, and long-term satisfaction. At Labrilliante, we've created this comprehensive buying guide to help you navigate the certified lab-grown diamond marketplace with confidence.
Price-Value Analysis: What You're Really Paying For
Understanding the true value proposition of different certification types helps optimize your investment:
Lab-Grown Diamond Certification Value Comparison
| Certification Body | Avg. Cost Premium | Key Value Adds | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| GIA Top global authority | 15–20% | Global recognition, strictest standards | Investment pieces, high-value items |
| IGI Pioneer in lab certification | 5–10% | Detailed inclusion maps, growth method specifics | Everyday luxury, engagement rings |
| GCAL Light performance specialists | 10–15% | Light performance analysis, cut optimization | Maximizing visual impact |
| Uncertified No verification | 0% | None | Not recommended |
| Labrilliante Recommendation: We prioritize IGI and GIA certification for optimal balance between thorough documentation and value. | |||
Value Distribution in Lab-Grown Diamond Pricing:
- Growth Technology: 40% of price (higher for larger, whiter diamonds)
- Cutting & Polishing: 25-30% of price (higher for complex shapes)
- Certification Costs: 5-10% of price
- Retail Operations: Remainder
At Labrilliante, we prioritize IGI and GIA certification for our lab-grown diamonds, as these provide the optimal balance between thorough documentation and value.
Decoding Certificate Information for Optimal Purchases
Learning to prioritize the most important certification information will help you make better buying decisions:
Primary Certification Factors (In Order of Importance):
- Cut Grade & Proportions
- Excellent/Ideal cut grades deliver maximum brilliance
- Pay attention to depth percentages (59-62.5% ideal) and table percentages (53-58% ideal)
- Look for symmetry and polish grades of "Excellent" or "Very Good"
- Color Grade in Context
- For white metals (platinum, white gold): E-F color delivers best value
- For yellow gold settings: G color appears white and offers significant savings
- Consider fluorescence as a potential value enhancer (medium blue fluorescence can make J color appear whiter)
- Clarity Considerations
- VVS2-VS2 clarity grades offer the best value proposition for lab-grown diamonds
- Eye-clean SI1 can provide exceptional value
- Review inclusion maps to ensure inclusions won't impact durability
- Certificate Details Checklist:
- Verify growth method is clearly stated (CVD or HPHT)
- Check for treatment disclosures (or confirmation of no treatments)
- Confirm presence of unique certificate number and verification method

Red Flags in Certifications: What to Avoid
Being aware of problematic certification issues protects your investment:
Warning Signs on Diamond Certificates:
- Vague terminology about clarity features (e.g., "cloudy" without specifics)
- Missing or ambiguous lab-grown origin statements
- Overly general cut descriptions without precise angles and proportions
- Certificates lacking online verification options
- Absence of growth method specification
- Missing or illegible plot diagrams
- Suspiciously high grades compared to price point
Diamond Certificate Reliability Hierarchy
| Reliability Tier | Certification Bodies | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Top Tier Maximum assurance | GIA, IGI, GCAL | Online report checking with full details |
| Mid Tier Acceptable reliability | GSI, HRD, AGS | Online verification of basic information |
| Low Tier Minimal reliability | In-house jeweler reports, unknown labs | Limited or no verification |
| Labrilliante Standard: We exclusively offer diamonds with top-tier certification to ensure complete transparency and confidence. | ||
At Labrilliante, we exclusively offer diamonds with top-tier certification to ensure complete transparency and confidence.
Matching Certification to Your Specific Needs
Different purchase scenarios might prioritize different certification aspects:
For Engagement Rings:
- Prioritize GIA or IGI certification with excellent cut grades
- Focus on eye-clean clarity (VS2 or better)
- Consider color grade in relation to setting metal
- Verify inclusion locations are away from areas where prongs will be placed
For Investment Pieces:
- GIA certification offers strongest resale value protection
- Opt for D-F color and VVS clarity for maximum future value
- Ensure growth method is explicitly documented
- Select rounds or classic shapes with excellent proportions
For Fashion Jewelry:
- IGI certification provides adequate documentation at value price point
- SI clarity grades offer excellent value when inclusions don't affect appearance
- Consider fancy shapes that maximize face-up appearance for the price

Expert Shopping Strategies from Labrilliante
Our team has developed these proven approaches to finding the best certified lab-grown diamonds:
- The Sweet Spot Strategy:
- Target F color, VS2 clarity, Excellent cut lab-grown diamonds
- Request videos under different lighting conditions
- Verify certificates through laboratory websites before purchase
- The Maximum Impact Approach:
- Prioritize cut quality over other factors
- Consider lower color grades (G-H) in yellow gold settings
- Reallocate budget to larger carat weight
- The Future Value Method:
- Select GIA-certified lab-grown diamonds
- Focus on classic shapes (round, oval, cushion)
- Maintain documentation in pristine condition
- Choose D-F color, VVS clarity for strongest value retention
At Labrilliante, our diamond experts can guide you through these strategies based on your specific preferences and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions: Lab-Grown Diamond Certification Insights
Yes, GIA fully certifies lab-grown diamonds with specialized reports. While they previously only issued "identification reports," GIA now provides comprehensive grading reports that include the 4Cs evaluation, growth method identification, and potential treatments. These reports use the term "Laboratory-Grown" and feature a distinct format from their natural diamond certificates.
Authenticate your certificate by visiting the issuing laboratory's official website and entering the certificate number in their verification portal. Most major labs (GIA, IGI, GCAL) offer free online verification tools. Check for security features like holograms, microprinting, and QR codes. Be wary if the seller refuses to provide the original certificate or if verification attempts return different information.
GIA certification is generally considered more stringent and carries a 15-20% price premium, while IGI certification provides detailed growth method information at a 5-10% premium. GIA uses more conservative grading standards, particularly for color and clarity, meaning an IGI-graded G color might receive an H from GIA. IGI reports often include more specific growth method details and inclusion maps, while GIA emphasizes rigorous origin verification.
Absolutely. Insurance companies typically require GIA or IGI certification for diamond coverage, as these documents establish verifiable value and identity. Many insurers offer specific riders for lab-grown diamonds at favorable rates compared to natural diamonds of equivalent specifications. The certificate's detailed documentation provides crucial proof for claims if loss or damage occurs. Always submit your certificate copies when applying for jewelry insurance.
While fluorescence is often considered a negative in natural diamonds, certain lab-grown diamonds—particularly HPHT types—can exhibit blue fluorescence that actually enhances color appearance by counteracting faint yellow tints. This creates a unique value proposition where medium fluorescence in I-J colored lab diamonds can make them appear whiter in daylight. Certification reports noting this feature can indicate a better value purchase, contrary to common assumptions.
Next-generation certification will likely incorporate AI analysis of growth patterns, providing more precise origin determination and quality assessments. Several certification labs are already developing machine learning algorithms that can detect synthetic diamonds and treatments with greater accuracy than human gemologists. Future certificates may include digital, blockchain-secured provenance tracking and real-time verification features. At Labrilliante, we're closely monitoring these innovations to ensure our certification processes remain cutting-edge.
Fancy colored lab-grown diamonds undergo specialized certification that evaluates hue, tone, and saturation rather than the D-Z color scale. Lab reports for these diamonds must explicitly disclose any color enhancement treatments (like irradiation or HPHT processing). Certification costs are typically 10-15% higher for fancy colors due to more complex spectroscopic analysis needed to determine color origin. GIA recently updated their colored lab-grown diamond reports to include detailed color distribution mapping.
While standard diamond certificates don't yet include carbon footprint data, specialized sustainability certifications are emerging. SCS Global Services now offers a "Certified Sustainability Rated Diamond" standard measuring energy consumption, water usage, and emissions during production. Forward-thinking manufacturers like Labrilliante are pursuing these optional sustainability certifications as supplements to traditional grading reports, documenting the 50-60% reduced carbon impact compared to mined diamonds.