Cut, polish and symmetry certification of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds have been gaining popularity as a more sustainable and ethical alternative to mined diamonds. However, the quality of lab-grown diamonds is highly dependent on the cut, polish, and symmetry of the diamond. This article will discuss the certification process for these three parameters and their significance in determining the overall quality of lab-grown diamonds.
Cut
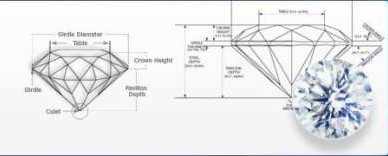
The cut of a diamond refers to the angles, proportions, and finishing of a diamond. It is one of the most important factors that affects the diamond's brilliance, fire, and overall beauty. A well-cut diamond will reflect the maximum amount of light, resulting in a bright and sparkling appearance.
To certify the cut of a lab-grown diamond, gemologists use a set of standardized measurements and calculations, including the crown height, pavilion depth, and table size. These measurements are then compared to established criteria for ideal cut diamonds to determine the cut grade. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is one of the most well-known organizations that certifies the cut of lab-grown diamonds.
Polish
The polish of a diamond refers to the surface finish of the diamond and how smooth it is. A well-polished diamond will have a smooth surface with no visible scratches or abrasions. The polish of a diamond can affect the diamond's overall appearance, as well as its durability.
To certify the polish of a lab-grown diamond, gemologists use a microscope to examine the diamond's surface for any defects. The defects are then rated on a scale, with the highest rating indicating a perfectly polished diamond. The GIA is also responsible for certifying the polish of lab-grown diamonds.
Symmetry
Symmetry refers to the balance and proportion of the diamond's facets and how they align with each other. A well-symmetrical diamond will have evenly spaced and aligned facets, which will result in a balanced and harmonious appearance.
To certify the symmetry of a lab-grown diamond, gemologists use a set of standardized measurements and calculations, including the alignment of the facets, the size and shape of the diamond's table, and the height of the crown. These measurements are then compared to established criteria for ideal symmetry to determine the symmetry grade. The GIA is also responsible for certifying the symmetry of lab-grown diamonds.
The cut, polish, and symmetry of lab-grown diamonds are crucial parameters that determine the overall quality of the diamond. A well-cut, well-polished, and well-symmetrical diamond will have maximum brilliance, fire, and overall beauty. The GIA is one of the most well-known organizations that certifies these parameters, ensuring that consumers receive a high-quality lab-grown diamond.