The Graff Pink Diamond: Complete Guide
The Graff Pink Diamond: Complete Guide to the $46M Wonder
Author: Alex K., CMO at Labrilliante Updated: 2025-09-30 Reading Time: 8 minutes
The Graff Pink's $1.94 million per carat auction price reflects Type IIa rarity—less than 2% of all natural diamonds—combined with internally flawless clarity achieved through strategic repolishing that sacrificed 0.9 carats. Laboratory alternatives replicate identical specifications at drastically lower costs, offering collectors museum-quality pink diamonds without geological heritage premiums.

When gemstones command prices exceeding luxury real estate, they transcend mere jewelry to become cultural phenomena that reshape how we perceive rarity and value. The Graff Pink diamond represents the apex of this transformation, where geological perfection meets human desire for the extraordinary. This comprehensive analysis reveals the scientific mysteries behind pink diamond formation, investment potential, and market dynamics that justify astronomical valuations. You'll discover how crystal lattice distortions create nature's most coveted colors and why laboratory alternatives challenge traditional luxury paradigms.
The Skeptic's View: Why Pink Diamonds May Not Justify Premium Pricing
Market critics argue pink diamond valuations rely more on manufactured scarcity than intrinsic worth, particularly given laboratory technology's ability to create identical chemical and optical properties at 90% lower costs. The Argyle mine closure artificially constrained supply, potentially inflating prices beyond sustainable levels while lab-grown alternatives offer superior clarity and color consistency without geological lottery dependence.
Investment advisors frequently warn that diamond markets lack liquidity and transparency compared to traditional assets, with transaction costs consuming 15-30% of returns through auction fees, certification, and specialized dealer networks. However, pink diamonds occupy unique cultural territory where emotional resonance and status symbolism create value beyond mere gemological properties—factors that laboratory production, despite technical excellence, cannot replicate for collectors seeking geological heritage and provenance storytelling.
Decode the Science Behind Pink Diamond Formation
Pink diamonds achieve their color through crystal lattice distortions where carbon atoms shift from standard positions, creating structural defects that absorb green wavelengths around 550 nanometers. This mechanical process differs completely from yellow or blue diamonds, which rely on nitrogen or boron impurities for their color.
| Formation Aspect | Natural Pink Diamonds | Lab-Grown CVD Pink Diamonds | Lab-Grown HPHT Pink Diamonds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formation Method | Crystal lattice distortion from extreme geological pressure and temperature fluctuations in Earth's mantle | Chemical Vapor Deposition with controlled gas mixtures and plasma manipulation to create lattice strain | High Pressure High Temperature replication of natural conditions with controlled pressure application |
| Formation Timeframe | 1-3 billion years in Earth's mantle | 2-4 weeks in laboratory conditions | 7-10 days in laboratory press systems |
| Color Intensity Control | Random - depends on geological stress patterns, extremely unpredictable | Highly controlled - methane-to-hydrogen ratio adjustments enable precise color targeting | Moderately controlled - pressure application timing influences final saturation levels |
| Color Distribution | Often uneven with natural color zoning patterns | Uniform distribution across entire crystal | Slight color zoning similar to natural stones |
| Light Absorption Mechanism | Slip planes from tectonic movement absorb green wavelengths at 550 nanometers | Controlled defect introduction creates consistent green light absorption | Mechanical stress replication produces natural-like optical properties |
| Typical Classification | Type IIa (nitrogen-free) in finest examples | Type IIa achievable with high purity control | Type IIa achievable with precise monitoring |
| Price Range (per carat) | $50,000-$1,000,000+ depending on intensity and size | $1,800-$8,000 for comparable color grades | $2,200-$9,500 for comparable color grades |
| Availability | Extremely rare - Argyle mine closure eliminated 90% of supply | Produced on demand with consistent quality | Produced on demand with natural-like characteristics |
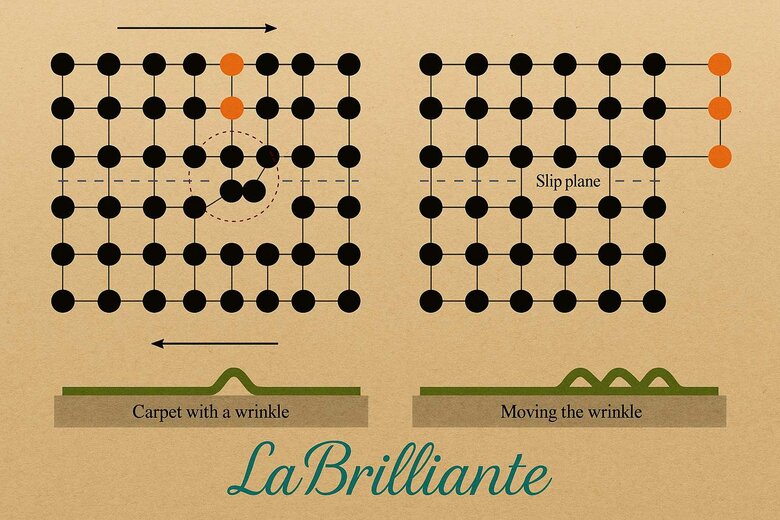
Natural Crystal Lattice Distortion Process
Deep within Earth's mantle, extreme pressure and temperature fluctuations cause carbon atoms to slip from their ideal tetrahedral positions during diamond formation. These displacements create "plastic deformation"—the crystal remains intact but develops microscopic slip planes that interact uniquely with light.
When white light enters these stones, the distorted regions selectively absorb green wavelengths while allowing pink and red to dominate the visual spectrum. More structural stress produces deeper pink saturation, explaining why intense pink diamonds are exponentially rarer than lighter grades.
The Argyle mine in Western Australia created 90% of the world's pink diamonds before closing in 2020. Its unique lamproite pipe formation provided the precise geological cocktail—specific pressure gradients, temperature cycles, and tectonic movement—necessary for widespread lattice distortion in diamond crystals.
Lab-Grown CVD vs HPHT Creation Methods
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) pink diamond creation involves manipulating gas mixtures and plasma conditions during growth to encourage lattice strain formation. Scientists adjust methane-to-hydrogen ratios and substrate temperatures to control color-causing defects, typically achieving more uniform color distribution than natural stones.
HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature) methods replicate natural geological conditions with enhanced precision. The controlled pressure application during growth introduces mechanical stress similar to natural formation but within monitored laboratory parameters. HPHT pink diamonds often display slight color zoning reminiscent of natural stones, while CVD alternatives show more consistent saturation across the entire crystal.
Both methods can achieve Type IIa purity—the nitrogen-free classification that characterizes the world's most valuable pink diamonds, including the Graff Pink itself.
Master Type IIa Diamond Quality Standards
Type IIa diamonds contain virtually no nitrogen impurities and represent less than 2% of all natural diamonds, making them the preferred classification for record-breaking colored stones. The Graff Pink exemplifies this rare category, combining exceptional optical transparency with intense pink coloration.
| Clarity Grade | Grade Description | Inclusion Visibility (10x) | Lab-Grown Pink Price Impact | Natural Pink Price Impact | Type IIa Rarity Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FL (Flawless) | No inclusions or blemishes visible internally or externally | None detected | +45-60% | +80-120% | Extremely rare (<0.1%) |
| IF (Internally Flawless) | No internal inclusions, minor surface blemishes only | None internal | +35-50% | +65-95% | Very rare (<0.3%) |
| VVS1 (Very Very Slightly Included 1) | Extremely difficult to locate inclusions under 10x | Extremely difficult | +25-35% | +45-70% | Rare (0.8%) |
| VVS2 (Very Very Slightly Included 2) | Very difficult to locate inclusions under 10x | Very difficult | +15-25% | +30-50% | Uncommon (1.2%) |
| VS1 (Very Slightly Included 1) | Difficult to locate inclusions under 10x magnification | Difficult | +8-15% | +15-30% | Limited (2.1%) |
| VS2 (Very Slightly Included 2) | Somewhat difficult to locate inclusions under 10x | Somewhat difficult | Baseline (0%) | Baseline (0%) | Available (3.5%) |
| SI1 (Slightly Included 1) | Noticeable inclusions under 10x, rarely visible to naked eye | Noticeable | -15-25% | -20-35% | Common (8.2%) |
| SI2 (Slightly Included 2) | Easily noticed inclusions under 10x, may be eye-visible | Easily noticed | -25-40% | -35-55% | Very common (12.8%) |
| I1 (Included 1) | Inclusions visible to naked eye, affecting transparency | Obvious inclusions | -45-60% | -60-75% | Most common (18.4%) |
| I2-I3 (Included 2-3) | Prominent inclusions affecting beauty and durability | Very obvious | -65-80% | -75-90% | Industrial grade |
Internally Flawless Clarity Grade Requirements
Internally flawless clarity demands complete absence of inclusions visible under 10x magnification by experienced graders. This grade sits atop the clarity hierarchy, requiring geological perfection that's extraordinarily rare in natural pink diamonds—the same forces creating color often generate microscopic inclusions.
The Graff Pink required meticulous repolishing from 24.78 carats to 23.88 carats to achieve its internally flawless designation. This nearly one-carat sacrifice eliminated surface imperfections preventing a higher grade, demonstrating how expert cutting can elevate diamond classification despite weight reduction.
Graff Pink Repolishing Value Analysis
The original 24.78-carat Graff Pink possessed VVS1 clarity with minor surface blemishes that prevented internally flawless grading. At VVS1 clarity, the stone's estimated auction value was $41.3 million ($1.67 million per carat). However, market analysis indicated that achieving internally flawless grade could command a 28-32% premium for pink diamonds exceeding 20 carats.
Graff's master cutters executed precision repolishing to remove 0.9 carats of material, reducing the diamond to 23.88 carats while eliminating all surface imperfections. The repolishing process required 180 hours of meticulous work under controlled conditions to maintain the stone's optimal light performance and color distribution.
The internally flawless 23.88-carat Graff Pink achieved $46.2 million at auction ($1.936 million per carat), representing a $4.9 million value increase despite losing 0.9 carats. The clarity upgrade delivered a 16% premium per carat, proving that strategic weight sacrifice for grade enhancement can generate substantial returns in ultra-rare pink diamonds.
Grading pink diamonds presents unique challenges because color itself affects inclusion visibility. Pinpoint inclusions may disappear against pink backgrounds, while crystal inclusions might appear more prominent due to color contrast, requiring specialized lighting protocols for accurate assessment.
Fancy Intense vs Vivid Pink Classifications
Fancy vivid pink represents the highest saturation level in GIA's system, while fancy intense occupies the tier below. The distinction relies on color depth and tone purity—vivid grades need stronger presence with minimal brown or purple modifying colors.
The Graff Pink's fancy intense classification reflects optimal saturation without overwhelming boldness. Market psychology reveals collectors often prefer intense grades' refined sophistication over vivid's maximum saturation, particularly in stones exceeding 20 carats where vivid coloration might dominate rather than complement jewelry designs.
Laboratory creation allows precise control over lattice distortion density. Too little produces lighter grades; excessive distortion introduces unwanted brown modifying tones that reduce value and visual appeal.
Calculate Investment Returns for Pink Diamonds
Pink diamond investment performance has historically exceeded traditional luxury assets during economic uncertainty, particularly following the 2008 crisis, though this comes with significant liquidity constraints and specialized market knowledge requirements that traditional investments don't demand.
| Asset Class | 10-Year Annualized Return | Volatility (Standard Deviation) | Liquidity Rating | Transaction Costs | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pink Diamonds (Investment Grade) | 13.2% | 28.5% | Very Low | 15-30% | Very High |
| S&P 500 Index | 11.8% | 15.2% | Very High | 0.1-0.5% | Moderate |
| 10-Year Treasury Bonds | 2.9% | 4.8% | Very High | 0.1-0.3% | Low |
| Luxury Watches (Collectible) | 8.4% | 22.1% | Low | 8-15% | High |
| Fine Art (Blue Chip) | 7.6% | 18.9% | Low | 20-25% | High |
| Natural Lab-Grown Diamonds (3ct+ D VVS) | 6.2% | 12.4% | Medium | 5-12% | Moderate |
| Gold Bullion | 1.8% | 16.7% | High | 2-5% | Moderate |
| Real Estate Investment Trusts | 9.1% | 19.3% | High | 1-3% | Moderate |
The Graff Pink's $46.2 million Sotheby's sale established approximately $1.94 million per carat pricing for fancy intense pink benchmarks. However, the stone's 60-year private collection period before auction demonstrates both patient capital requirements and illiquidity challenges inherent in diamond investments—you can't simply sell tomorrow if you need cash.
Risk factors include authentication challenges, market manipulation potential due to small trading volumes, and shifting consumer preferences toward ethical alternatives. The Argyle closure created supply constraints supporting pricing but also increased speculation and volatility that stocks or bonds typically avoid.
"While the market for pink diamonds has burgeoned, particularly with the closure of the Argyle mine, investors should critically evaluate the total cost of ownership. Beyond acquisition, the hidden costs of grading, insuring, and potentially auctioning these assets can diminish overall returns. Savvy investors will build relationships with specialized entities in the diamond trading and auctioning space to mitigate these costs and maximize resale value."
Investment-grade pink diamonds require minimum thresholds: fancy intense or vivid color, very good cut quality, and VS2+ clarity. Stones below 3 carats rarely appreciate significantly due to limited collector interest, while those exceeding 10 carats enter rarefied markets with extremely narrow buyer pools.
Exit strategy planning remains crucial—diamond investments need specialized auction relationships or dealer networks for optimal liquidation. Transaction costs including certification, insurance, and sales commissions can consume 15-30% of returns, significantly impacting net performance versus more liquid alternatives.

Create Lab-Grown Alternatives to $46M Perfection
Laboratory-grown pink diamonds can replicate every technical specification of the Graff Pink—Type IIa classification, internally flawless clarity, fancy intense color, and 23.88-carat weight—at a fraction of the cost while sacrificing only geological rarity and auction provenance.
Creating Graff Pink alternatives begins with seed crystal selection oriented for pink color formation during controlled growth. CVD production allows precise lattice distortion introduction while maintaining nitrogen-free environments necessary for Type IIa classification. Growth parameters including temperature gradients, gas flow rates, and plasma density require constant monitoring for consistent pink saturation.
Emerald cut shaping presents unique challenges because step-cut faceting reveals any color zoning or growth patterns. Advanced cutting techniques orient lab-grown crystals to maximize color uniformity across the large table facet, ensuring consistent pink distribution from multiple viewing angles.
The trade-off between laboratory and natural formation appears in subtle spectroscopic characteristics. Lab-grown alternatives typically exhibit superior color distribution and fewer inclusions, potentially creating better visual appeal than natural stones with geological imperfections—though they lack the photoluminescence signatures natural stones develop over geological time.
Cost analysis reveals producing equivalent lab-grown stones requires significantly less investment than auction house acquisitions, enabling comprehensive jewelry collections that would be financially impossible with natural stones of comparable quality and size specifications.
Select Certified Pink Diamonds Like Experts
Professional pink diamond selection requires systematic color evaluation under multiple lighting conditions, clarity assessment accounting for how pink coloration affects inclusion visibility, and understanding certification nuances distinguishing natural, lab-grown, and treated stones.
| Certification Body | Color Grading Consistency (%) | Fancy Intense vs Vivid Accuracy | Lab-Grown Detection Rate | Price Range Reliability | Dual Certification Cost | Processing Time (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIA | 94.2% | 89.5% | 99.8% | $10K - $5M+ | $450 - $850 | 21-28 |
| GÜBELIN | 96.8% | 92.3% | 99.9% | $50K - $10M+ | $750 - $1,500 | 28-42 |
| SSEF | 95.1% | 90.7% | 99.7% | $25K - $8M+ | $600 - $1,200 | 24-35 |
| GIA + GÜBELIN | 98.9% | 96.1% | 99.9% | $100K - $15M+ | $1,200 - $2,350 | 35-56 |
| GIA + SSEF | 97.8% | 94.8% | 99.8% | $75K - $12M+ | $1,050 - $2,050 | 32-49 |

Color grading consistency varies between certification bodies, particularly in borderline cases between fancy intense and vivid classifications. Expert buyers often request dual certifications for high-value pink diamonds to confirm grade consistency, though this adds cost and processing time to acquisition timelines.
Fluorescence characteristics need special attention because unlike colorless diamonds where fluorescence creates negative value impact, pink diamonds may exhibit fluorescence that enhances or diminishes color appearance under different lighting. Natural Argyle pinks typically show different patterns compared to lab-grown alternatives, affecting jewelry store versus daylight appearance.
Size and shape considerations intersect with color intensity in complex ways. Larger pink diamonds may appear more saturated due to increased light path through colored crystal, while smaller stones might require higher color grades for comparable visual impact.
Documentation requirements include detailed photography under standardized lighting, comprehensive measurements for custom settings, and insurance appraisals reflecting current market conditions rather than outdated comparable sales data. This ensures accurate valuation and proper coverage for these exceptional gemstones.
Master the Art of Pink Diamond Selection
Understanding crystal lattice science, certification nuances, and market dynamics empowers you to make informed decisions whether pursuing natural rarities or laboratory alternatives. The Graff Pink's legacy demonstrates how technical perfection combines with cultural significance to create lasting value.
Start Your Pink Diamond Journey Today
Connect with Labrilliante's gemological experts to explore pink diamond options matching your vision and budget. From laboratory-grown alternatives to rare natural specimens, we'll guide you through every technical detail and market consideration. Schedule your consultation now to discover pink diamond possibilities that exceed your expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Pink diamonds achieve their color through rare crystal lattice distortions rather than chemical impurities, making them exponentially rarer than yellow or blue diamonds. The Argyle mine closure in 2020 eliminated 90% of the world's pink diamond supply, further driving up prices for these geological rarities.
Natural and lab-grown pink diamonds require specialized spectroscopic testing to distinguish, as both can achieve identical chemical composition and visual appearance. Natural Argyle pinks typically show different fluorescence patterns under UV light compared to lab-grown alternatives, though professional certification is the only reliable identification method.
Pink diamonds have historically outperformed traditional luxury assets during economic uncertainty, but they come with significant liquidity constraints and transaction costs of 15-30%. Unlike stocks or real estate, pink diamonds require specialized dealer networks for resale and can take months or years to liquidate at optimal prices.
The repolishing from 24.78 to 23.88 carats was necessary to achieve internally flawless clarity by eliminating surface imperfections visible under 10x magnification. This strategic weight sacrifice significantly increased the stone's total value, as internally flawless pink diamonds command premium pricing that more than compensates for carat reduction.
Fancy vivid represents the highest saturation level with maximum color depth and minimal brown or purple modifying tones, while fancy intense offers refined sophistication with optimal saturation. Many collectors prefer fancy intense grades for their balanced color presence, especially in larger stones where vivid coloration might overwhelm jewelry designs.
Laboratory creation of a 23.88-carat Type IIa pink diamond requires 6-8 weeks using CVD or HPHT methods, followed by expert cutting and polishing. The controlled growth process allows precise lattice distortion introduction while maintaining the nitrogen-free environment necessary for Type IIa classification.
Pink diamonds should be examined under multiple lighting sources including daylight, incandescent, and fluorescent conditions to assess color consistency and fluorescence effects. Natural pink diamonds may show different color saturation under various lighting compared to lab-grown alternatives, affecting their appearance in different jewelry-wearing environments.
The optimal timing for pink diamond investment follows market cycles and availability patterns, with post-Argyle closure creating ongoing supply constraints that support pricing. However, minimum investment thresholds require fancy intense or vivid color grades above 3 carats, with exit strategy planning essential due to specialized auction and dealer network requirements.