Colored Lab Grown Diamonds: Money Saving Guide
Colored Lab Grown Diamonds: Full Spectrum of Shades Available
Author: Alex K., CMO at Labrilliante Updated: 2025-10-06 Reading Time: 8 minutes
Lab-grown colored diamonds offer 70-97% savings versus natural stones through CVD and HPHT manufacturing methods that control trace elements like nitrogen and boron. Blue and pink varieties show the greatest price advantages, with two-carat lab pinks costing less than half-carat natural equivalents while achieving identical professional grading standards.

Modern couples increasingly reject cookie-cutter engagement traditions in favor of personalized expressions that reflect their unique love stories. Colored lab grown diamonds represent this cultural shift toward authenticity and individual style, offering couples the chance to celebrate with stones as distinctive as their relationships. Beyond romantic symbolism, these scientifically-created gems deliver unprecedented access to rare colors once reserved for royalty and Hollywood elite. You'll discover how cutting-edge manufacturing unlocks every shade imaginable while delivering exceptional value that transforms luxury shopping into smart investment decisions.
The Traditional Purist Perspective: Why Natural Formation Still Matters
Diamond traditionalists argue that geological rarity creates intrinsic value that laboratory manufacturing cannot replicate, regardless of visual similarities. They contend that billions of years of natural formation processes imbue stones with emotional significance and investment potential that lab-created alternatives inherently lack. This perspective particularly resonates with buyers viewing diamonds as generational heirlooms rather than contemporary fashion statements.
While this romanticism around natural origin holds appeal for certain demographics, market data reveals shifting consumer priorities toward ethical sourcing and value optimization. The "rarity equals value" argument weakens when considering that most natural colored diamonds remain locked in private collections or museums, making lab alternatives the only practical path to ownership for most buyers. Additionally, identical chemical composition and superior clarity often make lab diamonds more visually impressive than their natural counterparts, delivering better actual performance despite philosophical preferences for geological formation.
CVD and HPHT Methods Create Every Diamond Color
Lab technology produces colored diamonds by controlling carbon arrangements and adding trace elements during growth. Two manufacturing methods—CVD and HPHT—create the complete color spectrum through precise impurity placement in the diamond crystal structure.
| Production Method | Temperature | Pressure | Production Time | Cost per Carat | Best Color Capabilities | Color Formation Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | 800-900°C | Low pressure (below 1 atmosphere) | 2-4 weeks | $400-800 | Yellow, Orange, Pink, Light Blue | Layer-by-layer growth with nitrogen and silicon impurities |
| HPHT (High Pressure High Temperature) | 1300-1600°C | 50,000+ atmospheres | 1-2 weeks | $500-900 | Vivid Blue, Intense Yellow, Brown | Boron and nitrogen integration during high-pressure crystallization |

Chemical Vapor Deposition Color Formation Process
CVD builds diamonds layer by layer at 800-900°C using methane and hydrogen gases. Color develops when trace elements integrate during growth—nitrogen creates yellow to orange stones, while vacancy-nitrogen combinations produce pink diamonds.
The process flows gases over diamond seeds in controlled chambers. Silicon impurities generate blue tones, though boron produces more predictable results. Post-growth treatments through irradiation and annealing can intensify colors or create new color centers.
Trade-off consideration: Enhanced stones may lose "as-grown" designation that some buyers prefer, though color improvements often justify this compromise.
High Pressure High Temperature Trace Element Control
HPHT replicates natural formation with 50,000+ atmosphere pressure and 1300°C+ temperatures. This method excels at blue diamond production through boron integration during the growth phase.
Boron atoms substitute into the diamond lattice, creating electronic properties that absorb red wavelengths. Concentration determines intensity—low parts-per-million levels produce light blue stones, while higher concentrations achieve vivid blues matching premium natural specimens.
Extended high-temperature exposure allows nitrogen clustering into N3 centers. This creates intense yellow saturation often exceeding CVD-grown yellows.
Nitrogen and Boron Impurity Color Creation
Nitrogen produces the widest color range from champagne to canary yellow. Single nitrogen atoms create different properties than nitrogen pairs or clusters, spanning yellow, orange, and brown tones.
Higher nitrogen levels risk clarity impacts through visible inclusions. Modern methods balance color intensity against transparency requirements for gem-quality stones.
Boron creates coveted blue diamonds with semiconductor properties. Pure blues require exceptionally clean environments—trace impurities shift color toward gray or green undertones.
"While both CVD and HPHT methods facilitate the creation of beautiful colored diamonds, its critical to understand that the choice of trace elements and their precise integration into the diamond lattice not only dictates the resultant hue but also affects the optical properties and market value of the diamonds. For instance, integrating boron in HPHT processes not only cultivates rich blue tones but notably enhances the diamonds conductivity, a feature highly valued for certain technological applications beyond jewelry."
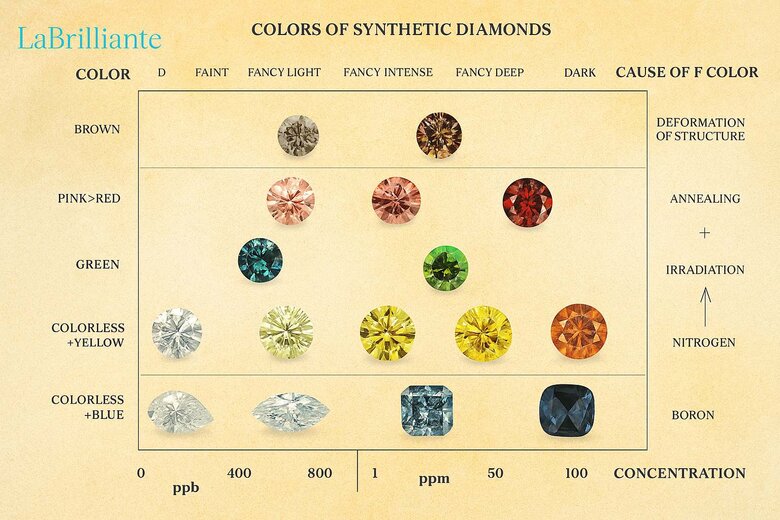
Complete Color Spectrum and Professional Grading Standards
Lab diamonds achieve every gemological color through controlled manufacturing. Professional certification applies identical grading standards to lab-grown stones, using the same fancy color classification system developed for natural diamonds.

Fancy Vivid to Fancy Intense Classification
Color grading follows standardized progression from Faint through Fancy Vivid. Each grade represents measurable saturation differences that trained gemologists consistently identify under controlled lighting conditions.
Fancy Vivid shows maximum saturation with pure, intense color. Fancy Intense demonstrates strong color with slightly reduced saturation. Fancy Light and Fancy grades offer attractive middle-range options at accessible price points.
Lab diamonds often achieve higher color grades than natural stones due to controlled environments minimizing unwanted secondary hues. However, some buyers still prefer natural formation despite manufacturing advantages.
Professional certification remains essential—subtle color differences significantly impact value and buyer confidence. Trusted laboratories ensure grades reflect standardized criteria rather than marketing claims.
Blue to Pink Diamond Color Range
Blue lab diamonds span pale sky tones to intense ocean depths through controlled boron concentrations during HPHT growth. Gray-blue combinations offer sophisticated alternatives when trace hydrogen or other impurities modify the boron spectrum.
Pink diamonds range from subtle blush tones to romantic intensities. Color develops through vacancy-nitrogen defect centers created via controlled irradiation and annealing cycles requiring precise timing.
Red diamonds represent the pink spectrum's extreme end. Extended treatment processes concentrate color centers while maintaining clarity—making reds among the most technically challenging to manufacture consistently.
Green stones emerge from controlled irradiation creating specific defect centers. Yellow diamonds range from pale champagne to golden hues capturing sunny warmth for various jewelry applications.
Smart Buying Guide for Colored Lab Diamonds
Colored diamond selection balances color intensity against size and clarity considerations. Unlike colorless diamonds where cut and clarity dominate, colored stones prioritize color grade as the primary value factor.
| Color Family | Color Grade Priority | Size Priority | Clarity Priority | Cut Priority | Optimal Investment Range (ct) | Price Premium vs Colorless (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow | Very High (85%) | Medium (60%) | Low (40%) | Medium (65%) | 1.5-3.0 ct | +25-40% |
| Pink | Critical (95%) | Low (45%) | Low (35%) | High (75%) | 1.0-2.5 ct | +60-120% |
| Blue | Critical (90%) | Medium (55%) | Medium (50%) | High (80%) | 1.2-2.8 ct | +45-85% |
| Green | Very High (88%) | Low (50%) | Medium (55%) | Very High (85%) | 1.0-2.0 ct | +80-150% |
| Orange | High (80%) | Medium (65%) | Low (45%) | Medium (70%) | 1.8-3.5 ct | +35-65% |
| Purple | Very High (85%) | Low (40%) | Low (35%) | High (75%) | 1.0-2.2 ct | +70-110% |
| Red | Critical (98%) | Very Low (30%) | Very Low (25%) | Very High (90%) | 0.5-1.5 ct | +200-400% |
| Champagne/Brown | Medium (70%) | High (75%) | Medium (60%) | Medium (65%) | 2.0-4.0 ct | +10-25% |
Key trade-off: Fancy Vivid grades in smaller sizes often provide more visual impact than larger Fancy Light stones, particularly in yellow and pink diamonds where saturation drives emotional appeal.
Certification proves critical for colored diamonds requiring specialized expertise. IGI and GIA provide standardized assessment ensuring consistent evaluation across viewing conditions and markets.
Shape affects color appearance significantly. Cushion and radiant cuts concentrate color centrally, while emerald cuts display color evenly but may appear less saturated. Round brilliants often dilute intensity through their light return patterns.
Setting choices dramatically impact presentation. Yellow gold complements yellow diamonds while potentially clashing with blues. Platinum and white gold provide neutral backgrounds allowing pure color expression across all hues.
Professional verification protects against color-treated naturals misrepresented as high-grade colored diamonds—a distinction significantly affecting both cost and long-term value.
Cost Advantages and Value Analysis Compared to Natural
Colored lab diamonds deliver 70-97% cost savings versus equivalent natural stones. Most dramatic advantages appear in rare colors like vivid blue and pink where natural specimens command astronomical premiums.
Savings vary by color family: Blue lab diamonds offer greatest differentials since natural blues rank among rarest geological formations. Yellow lab diamonds provide moderate savings as natural yellows occur more frequently.
2-Carat Pink Diamond Cost Comparison Analysis
A collector seeking a 2-carat Fancy Intense pink diamond for an heirloom engagement ring faced a $180,000 price quote from Sotheby's for a natural stone with VS1 clarity and excellent cut. The budget constraints meant considering a smaller 0.8-carat natural alternative at $65,000, significantly compromising the desired visual impact and symbolism.
The buyer evaluated a laboratory-grown 2-carat Fancy Intense pink diamond with identical VS1 clarity, excellent cut proportions, and Type IIa crystal structure. The lab diamond displayed the same vivid saturation and fire characteristics, certified by GIA with matching color grade specifications.
The lab-grown option cost $45,000—delivering 75% savings or $135,000 in immediate value. This price differential enabled upgrading to the full 2-carat target size while maintaining $20,000 under the original smaller natural stone budget. The buyer achieved 2.5x larger surface area (150% more visual presence) while accessing premium setting options with the saved capital.
This creates strategic opportunities. A two-carat fancy intense pink lab diamond costs less than a half-carat natural equivalent, enabling buyers to prioritize size and visual impact over geological origin.
Reality check: Lab diamonds focus on immediate enjoyment rather than appreciation potential. This appeals to buyers viewing jewelry as personal luxury rather than financial assets—particularly millennials prioritizing ethical consumption over traditional status symbols.
Value optimization targets color grades providing optimal visual impact relative to certification premiums. Fancy Intense often represents the sweet spot where saturation satisfies aesthetic goals without Fancy Vivid premiums that may offer marginal improvements.

Current Trends and Seasonal Applications for Colored Diamonds
Pink and blue stones dominate engagement season from November through February as couples seek personalized uniqueness over traditional colorless preferences. Spring extends this trend with buyers gravitating toward yellow and green diamonds echoing renewal themes.
Sustainability consciousness drives increasing lab-grown acceptance among millennials researching supply chain transparency before luxury purchases. This demographic shift creates opportunities for colored diamonds aligning values-based decisions with aspirational elegance.
Visual advantage: Colored stones photograph dramatically for social sharing compared to colorless diamonds appearing indistinguishable in smartphone images. This distinctiveness drives demand among buyers valuing Instagram-worthy aesthetics.
Fall 2024 emphasizes earth-toned diamonds including champagne, cognac, and olive shades complementing seasonal fashion palettes. Holiday gifting shows increased colored diamond demand as buyers seek distinctive alternatives to conventional purchases.
Looking ahead: 2025 predictions suggest continued growth in unconventional hues like gray-blue combinations and peach-pink variants offering subtle differentiation while maintaining broad appeal.
Eco-consciousness increasingly influences selection as sustainability becomes standard rather than exceptional among luxury consumers. Conflict-free laboratory sourcing addresses ethical concerns while delivering modern sophistication appealing to buyers balancing personal desires with social responsibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
Colored lab diamonds offer 70-97% savings versus equivalent natural stones, with the greatest savings found in rare colors like vivid blue and pink. A two-carat fancy intense pink lab diamond costs less than a half-carat natural equivalent, enabling buyers to prioritize larger sizes and better visual impact.
Lab diamonds achieve different colors through controlled trace elements added during the CVD or HPHT manufacturing process. Boron creates blue diamonds, nitrogen produces yellow to orange stones, and vacancy-nitrogen combinations generate pink diamonds through precise impurity placement in the crystal structure.
Yes, professional certification laboratories like GIA and IGI apply identical grading standards to lab-grown colored diamonds using the same fancy color classification system. The grading follows the same progression from Faint through Fancy Vivid based on measurable saturation differences under controlled lighting conditions.
Cushion and radiant cuts concentrate color centrally for maximum intensity, while emerald cuts display color evenly but may appear less saturated. Round brilliants often dilute color intensity through their light return patterns, making them less ideal for showcasing vivid colors.
The manufacturing method primarily affects production efficiency rather than final appearance, though HPHT excels at creating intense blues through boron integration while CVD produces excellent pinks and yellows. Both methods can achieve identical professional grades and visual results in most color ranges.
Lab diamonds focus on immediate enjoyment rather than appreciation potential, appealing to buyers who view jewelry as personal luxury rather than financial assets. This approach particularly resonates with millennials prioritizing ethical consumption and visual impact over traditional investment considerations.
Fancy Intense often represents the optimal balance where color saturation satisfies aesthetic goals without the premium pricing of Fancy Vivid grades that may offer only marginal visual improvements. Prioritize color grade over size in colored diamonds since saturation drives emotional appeal and visual impact.
Peak demand occurs from November through February during engagement season, with spring extending the trend as couples seek personalized alternatives. Fall offers opportunities for earth-toned diamonds like champagne and cognac that complement seasonal fashion palettes and holiday gifting preferences.